Condition monitoring and Predictive Maintenance (PdM) form the foundation of what we now know as Industrial IoT (IIoT) or Industry 4.0. It’s common to assume that both terms mean the same thing, but the reality is, they are very different.
Condition monitoring involves monitoring a specific parameter (vibration, temperature, pressure, etc.), to identify any significant changes from the norm which could indicate potential equipment failure.
Predictive maintenance, on the other hand, is the process of analyzing data to identify patterns and predict any issues before they occur. It’s important to note that an integral part of condition monitoring is providing the data that can then be used for PdM.
Maintenance is a major concern when developing and manufacturing a product. Consider all the resources involved to ensure that these assets are running smoothly and at optimal efficiency. For machine operators and factory personnel, asset repairs consume unnecessary resources, increase overall operational costs and present a serious impediment to efficient operations. Consequently, this means higher labor costs, reduced customer satisfaction and a competitive disadvantage.
How is Bluetooth technology involved?
So, how does Bluetooth play a role in condition monitoring and PdM? Bluetooth technology has emerged as a wireless connectivity solution because it’s low cost, provides easy remote management of assets and reduces the wiring costs associated with cabling. Furthermore, with a wireless connectivity solution, equipment now becomes smart equipment which allows us to continuously monitor the health of the equipment and plan ahead for any maintenance issues.
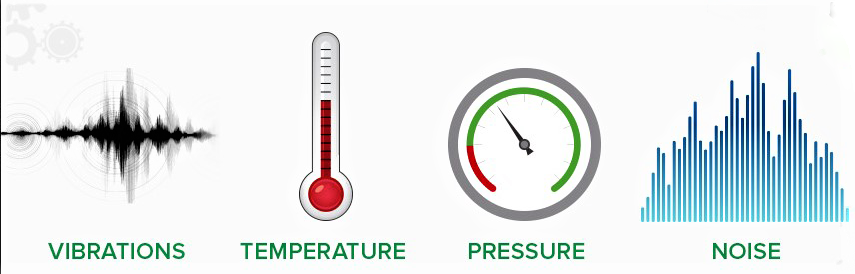
To provide a little background information on predictive maintenance, it’s important to discuss how sensors play a role. First, a sensor is the first and most important component of the entire system. There are different types of parameters that a sensor can measure. The most common ones are vibration, temperature, pressure, and current. The figure1 below shows a sensor that measures such parameters.
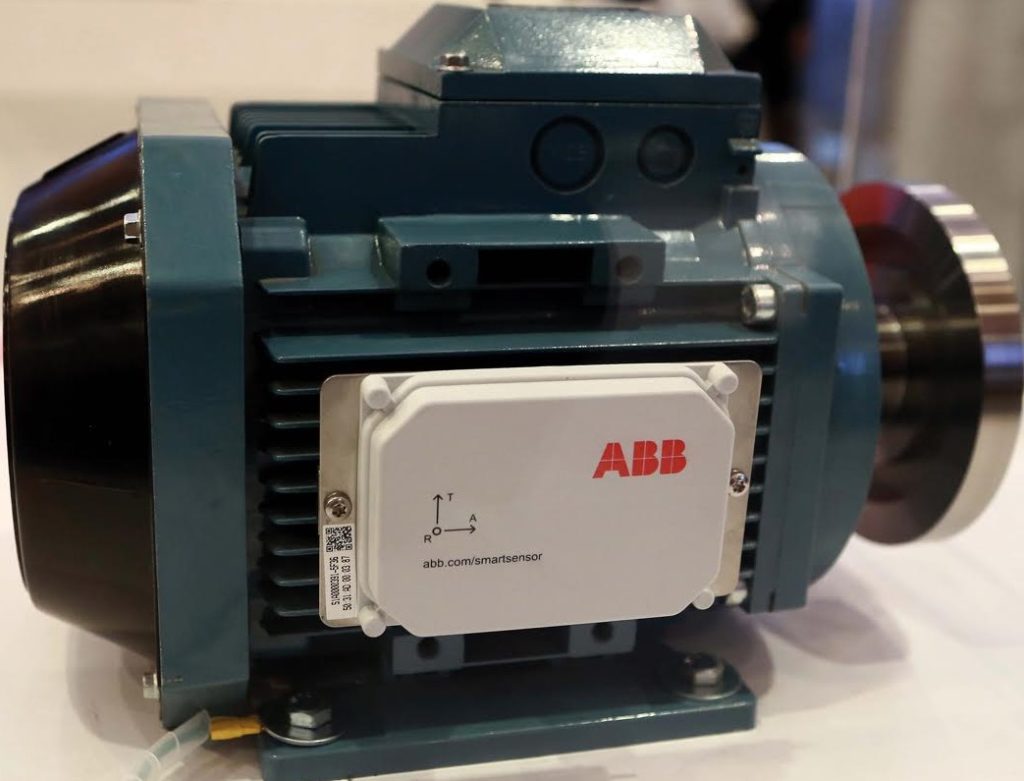

An effective monitoring system requires both the hardware and software components which should include condition monitoring sensors and gateways (the hardware) that will handle data processing and transmission, and a secured cloud server (the software) that will handle the data storage and data analytics.
The sensors are placed on the machines as seen in Figure 1, and a wireless gateway (seen below in Figure 2) will collect the data from the sensors and send it to a management system for further analysis. If the sensors detect any machine anomalies, the user will receive an alert and perform any maintenance if needed. The depth of data that is collected provides manufacturers with extremely valuable information that can be leveraged to make informed business decisions to reduce the impact of equipment breakdowns, unscheduled maintenance, failures, etc.
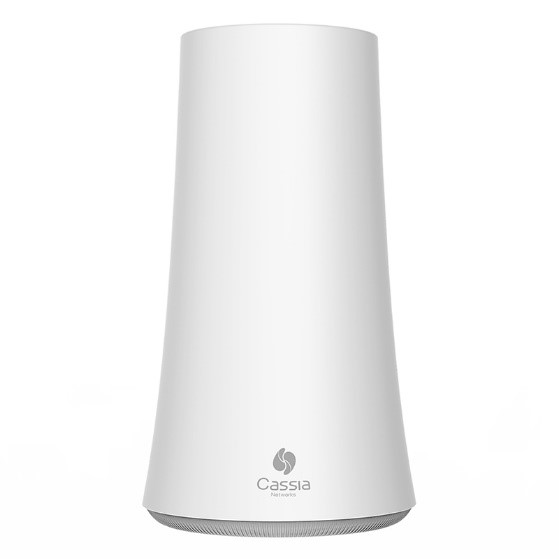

This is the core of predictive maintenance and is one of the main factors driving IIoT. By having a proactive rather than reactive approach, factories worldwide will become more efficient, productive, reduce unplanned downtime and minimizes long-term costs.
The future of Bluetooth technology
Industries such as IIoT, education and healthcare are using Bluetooth technology because of its ease of management, wireless connectivity and low cost. Bluetooth-powered IoT can be a big differentiator for companies looking to reduce manual tasks and enhance operational efficiency. Organizations with a well-planned IoT strategy and an understanding of Bluetooth technology use cases will definitely gain a competitive edge and improve their bottom line.