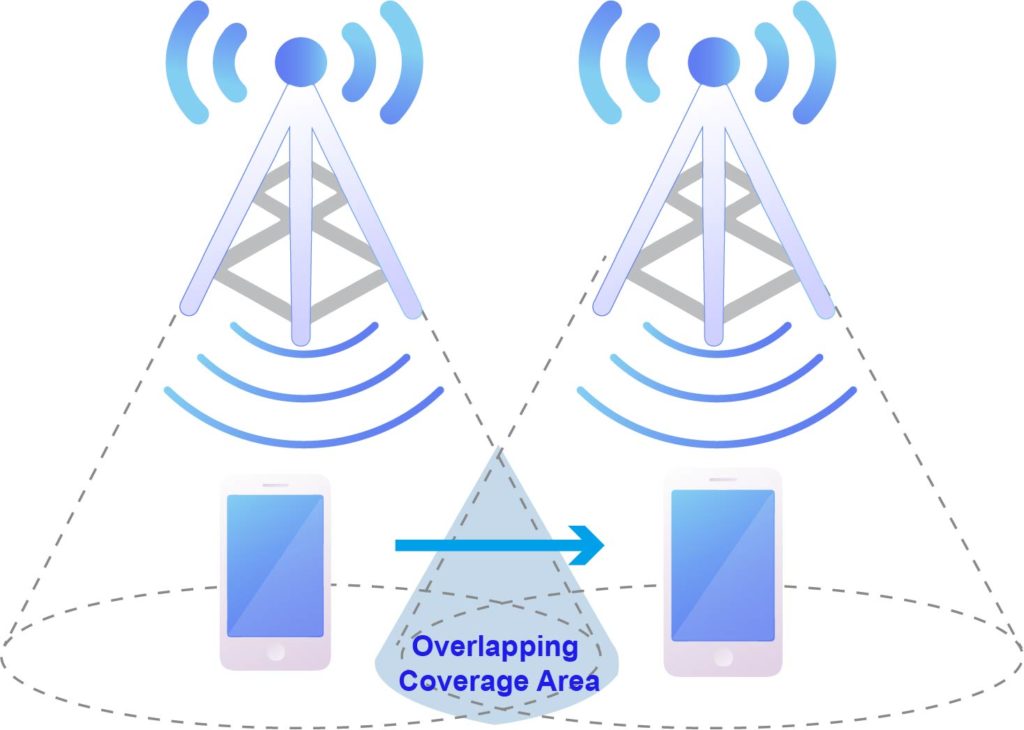
Most of us are familiar with wireless roaming and how it works, but let’s cover some of the basics. Roaming occurs when a wireless client device moves outside of a range of one wireless access point (AP) and connects to another AP with a stronger signal. As long as the AP’s are correctly setup and configured, client devices can roam seamlessly from one AP to another to ensure that data isn’t lost and connectivity remains continuous.
The challenge oftentimes resides in the “handoff” process which is dictated by the client device. The handoff is the process of the client device disconnecting from one AP and then re-associating it with another AP. This process consists of 3 phases: scanning, authentication and re-association. Provided that the AP’s are set up correctly, the handoff process typically takes less than 500 milliseconds (less than ½ second). However, the biggest delay occurs during the scanning phase when devices are moving from a connected AP to another based on the RSSI values.
Why is there a delay?
Roaming is dependent on the client device’s roam trigger. In other words, the client decides when it’s time to drop one AP and move to another. Therefore, some devices will measure RSSI values (which may take a little longer) before roaming to a new AP.
Is Roaming possible with Bluetooth?
Bluetooth technology does not support any sensor protocol which is related to roaming. Essentially, the handoff that would typically occur when a Bluetooth device is moving away from the coverage of the network doesn’t exist with Bluetooth. For example, if a device is losing its connection to the master device, there is no provision which transfers it to another master.
How Cassia has revolutionized Bluetooth Roaming
Cassia’s patented Bluetooth Roaming technology allows for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) devices to roam freely and securely within Bluetooth coverage areas without losing connectivity. Therefore, BLE devices such as sensors and tags can now move freely within the network and remain connected. What’s more, there is no need for manual intervention to ensure BLE devices remain connected and secure.
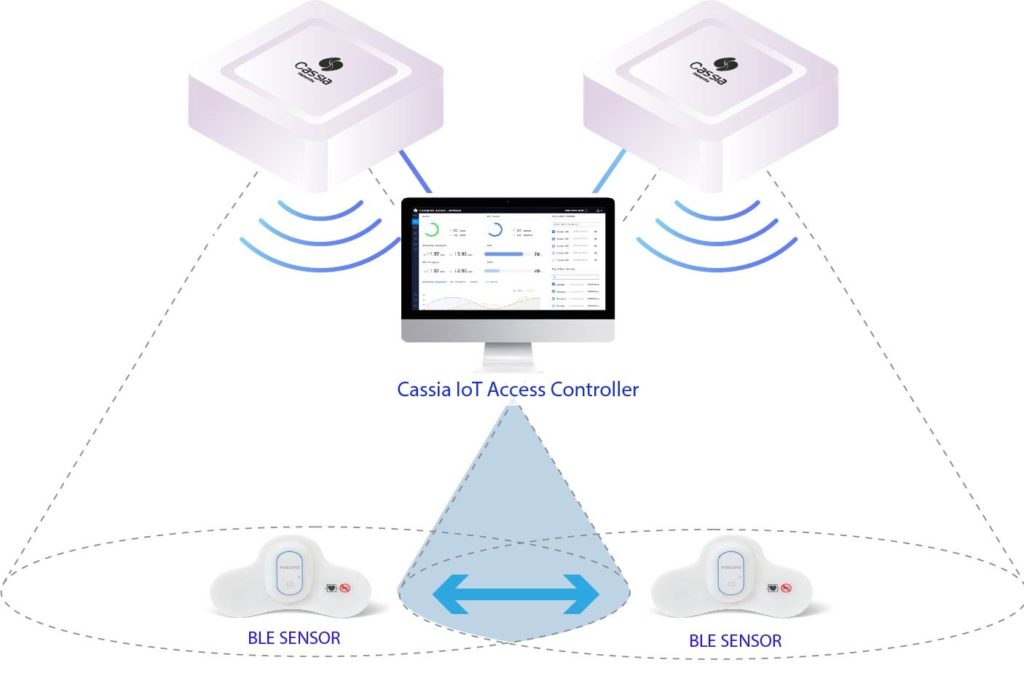
Cassia’s IoT Access Controller (AC) seen above, is the central intelligence that controls all of the gateways in a BLE network. All gateways under the IoT AC will function as a single gateway without user intervention. A unique algorithm assigns the necessary security credentials to the gateways to allow for a secure and seamless handoff.
What are the possible applications with Cassia’s Bluetooth Roaming technology?
The possibilities are endless with Cassia’s Bluetooth Roaming technology. Any mobile Bluetooth IoT application that requires devices to move can benefit from Bluetooth Roaming. For example, smart hospitals equipped with hundreds of BLE medical sensors and/or tags can benefit from using Bluetooth Roaming to ensure a secure and seamless handoff with continuous connectivity.
Want to learn more about this groundbreaking technology? Contact our sales team at sales@cassianetworks.com.








